AI is in the portfolio, and now it’s time to think about the next big thing. There are many advances in many fields but they are too far away to my knowledge, the closer one where I have some literacy is technology, so I have picked Quantum Computing as a field where to read.
When is Quantum computing to achieve relevant results? I have no clue, but there are many companies investing and advancing on this field and it could be that from here to 2030 many things can happen.
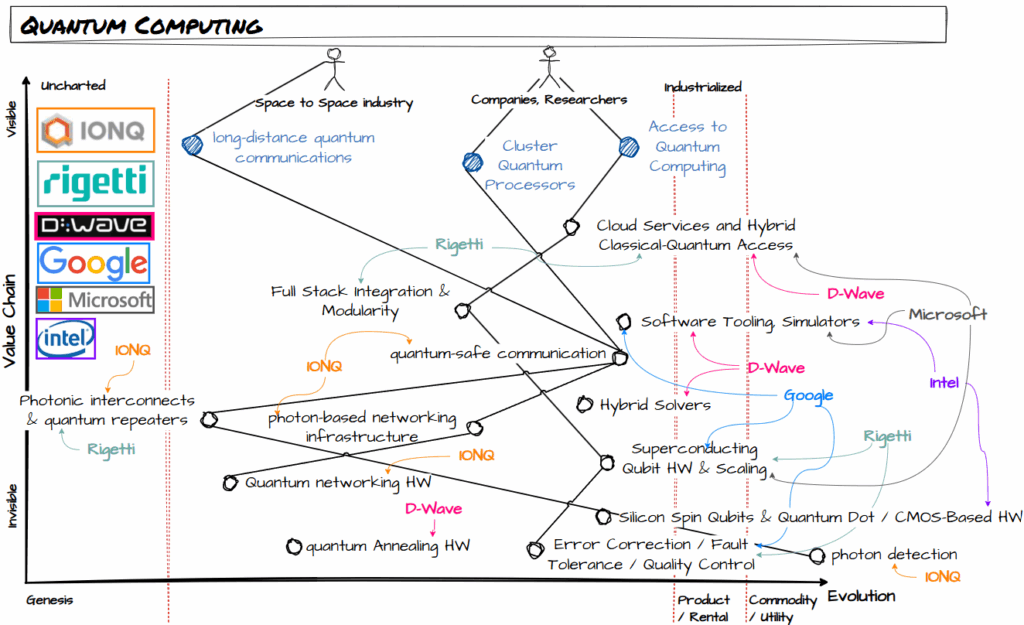
I have been reading about Quantum Computing, and with the purpose of organize ideas, I did a Wardley Map for it.
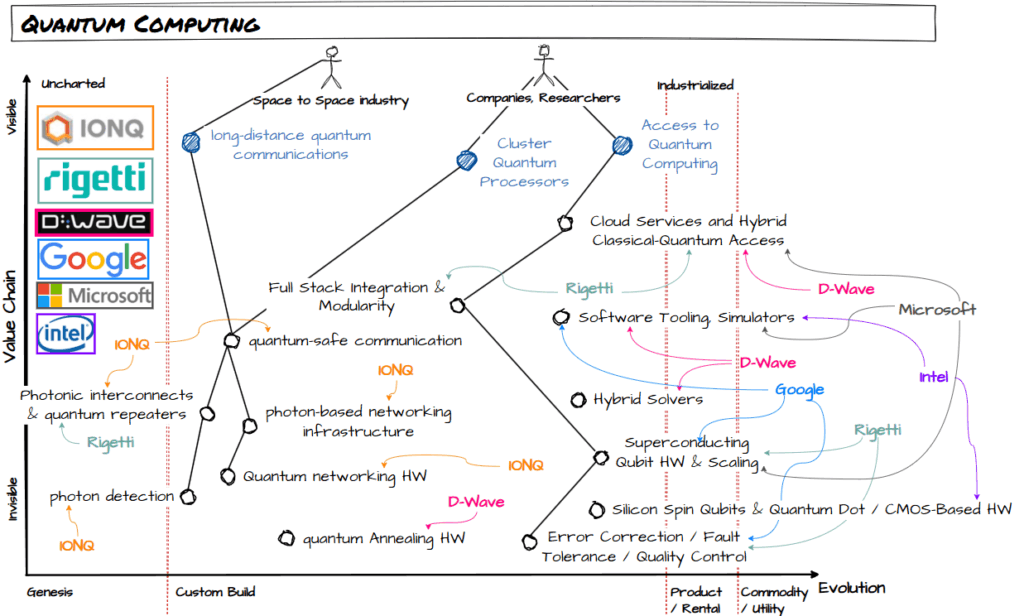
I have selected public companies, as they are forced to publish financial data and be accountable in front of the regulator. There are many other companies, but I lack of time to review all.
After observing the map, it’s interesting to see how IONQ and a little bit Rigetti are the ones that are doing something different: heavily invested in communications. The major players are focused on processors, software (there’s a world of new software here that probably deserves another map) and cloud and on-premise services.
There are 2 groups of companies playing the game: big corporations and medium size corporations that are nurtured by investors and have small or nule revenue.
What is the financial profile of the medium size companies?
I did a review of the 3 of them: Rigetti, D-Wave and IonQ, and they are similar:
Small revenue, high-operating cost…
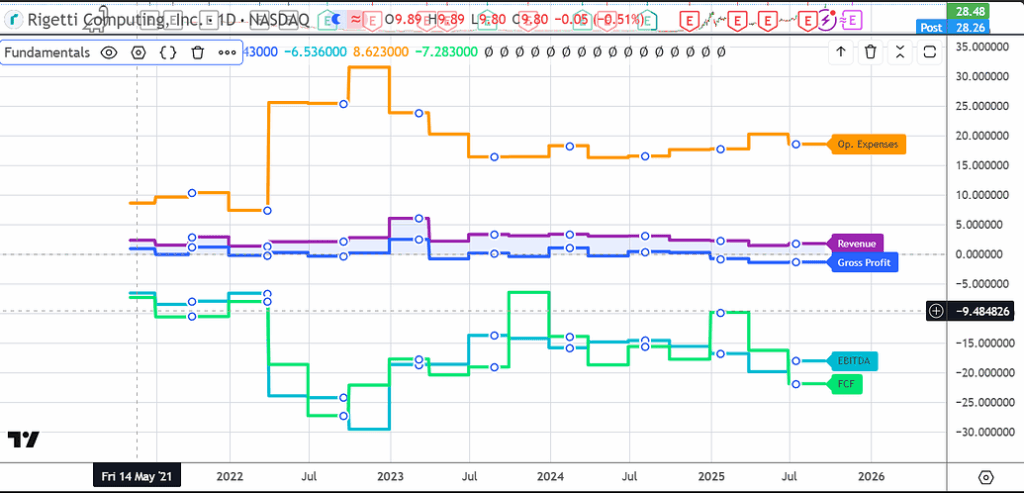
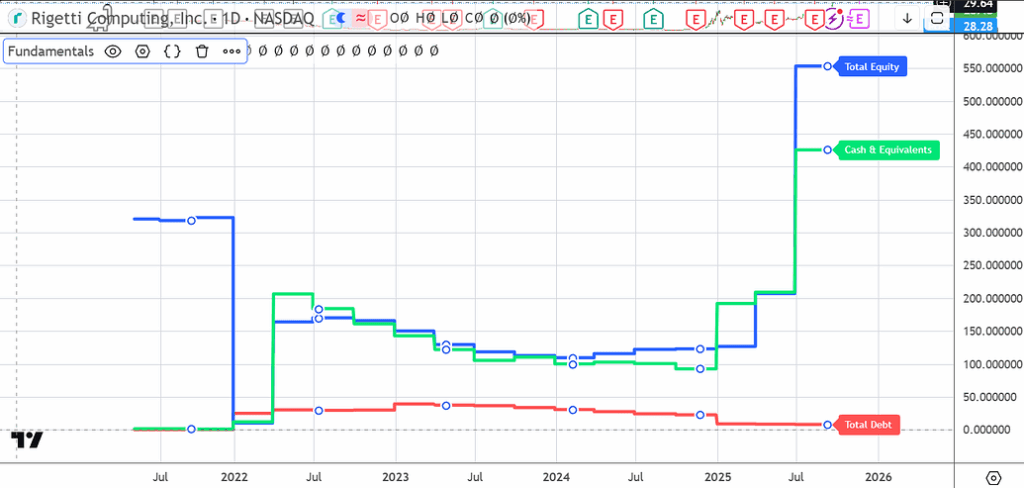
High valuations, small amount of debt, a lot of cash secured from investors
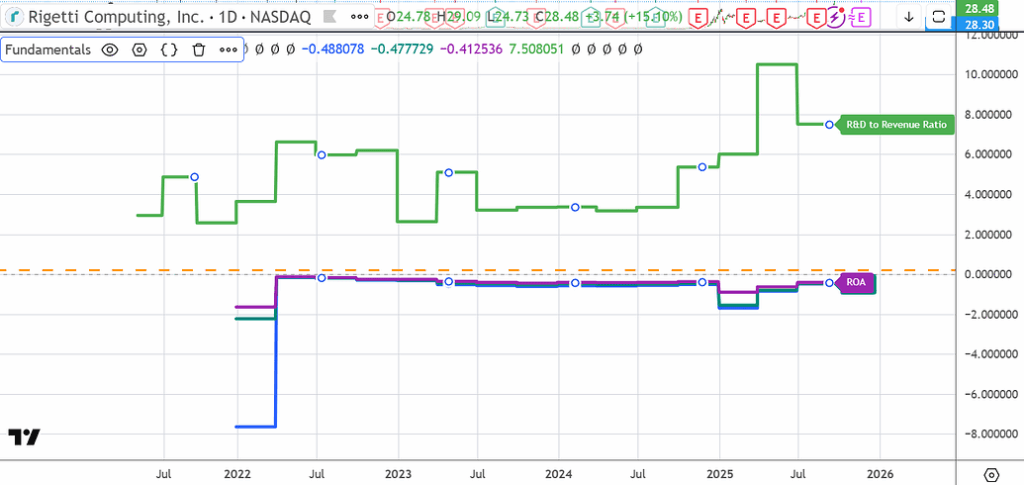
Too much amount of R&D, and negative returns
What are the ETFs doing?
As I’m new on this field, I wanted to know what the ETFs of the sector doing.
VanEck Quantum Computing UCITS ETF (QNTM)
| Rank | Company | Approx % Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IonQ, Inc. | ~8.5 % |
| 2 | D-Wave Quantum, Inc. | ~4.6 % |
| 3 | Intel Corporation | ~4.2 % |
| 4 | Wells Fargo & Co. | ~4.2 % |
| 5 | Bank of America Corp. | ~4.1 % |
| 6 | Microsoft Corp. | ~4.1 % |
| 7 | IBM | ~4.1 % |
| 8 | Honeywell International, Inc. | ~4.0 % |
| 9 | Amazon.com, Inc. | ~4.0 % |
| 10 | Synopsys, Inc. | ~4.0 % |
WisdomTree Quantum Computing UCITS ETF (WQTM)
| Rank | Company | Approx % Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IonQ, Inc. | ~6.3-6.5 % |
| 2 | Rigetti Computing, Inc. | ~5.6-6.0 % |
| 3 | D-Wave Quantum, Inc. | ~5.0-5.6 % |
| 4 | Quantum Computing Inc. (Ticker: QUBT) | ~4.0-4.5 % |
| 5 | Intel Corporation | ~4.1-4.2 % |
| 6 | Alphabet Inc. (Class A) | ~3.9-4.0 % |
| 7 | Amazon.com, Inc. | ~2.9-3.5 % |
| 8 | Fujitsu Limited | ~3.3 % |
| 9 | Microsoft Corporation | ~3.2-3.3 % |
| 10 | IBM | ~2.9-3.3 % |
Updated map 21/Sept
Updated following inputs from Sergey,
Are these companies scam?
I did a random walk on Twitter searching for “D-Wave scam”, “ionq scam” y “Rigetti scam”. All of them have people announcing their technology is a scam. The one with more and worst comments is D-Wave.
Definition of the Components on the map
As there are many new concepts, I have given a definition to each component to have better understanding and when sharing the map.
- Cloud Services and Hybrid Classical-Quantum Access: Cloud platforms that allow users to run quantum algorithms while integrating with classical computing resources, often providing hybrid workflows to maximize performance.
- Full Stack Integration & Modularity (HW – MW – SW Integration): Combining quantum hardware, middleware, and software layers into an interoperable stack, while allowing modular components (e.g., hardware choice, error correction, developer tools) to be swapped or integrated.
- Software Tooling, Simulators: Development environments, SDKs, and simulators that let researchers and developers design, test, and run quantum algorithms on classical hardware before deploying to actual quantum devices.
- Quantum-Safe Communication: Cryptographic methods resistant to attacks from quantum computers (e.g., lattice-based cryptography, quantum key distribution) to secure digital communication.
- Photonic Interconnects & Quantum Repeaters: Devices that transmit and extend quantum states (qubits) across optical fibers or free space, enabling long-distance quantum communication by overcoming photon loss and decoherence.
- Photon-Based Networking Infrastructure: The backbone for transmitting quantum information using photons as carriers, including optical fibers, switches, and other photonic network components.
- Quantum Networking HW: Specialized hardware (e.g., quantum routers, transceivers, memories) that enables qubit transfer and entanglement distribution across quantum networks.
- Photon Detection: Hardware that detects single photons with high efficiency and low noise, crucial for quantum communication, networking, and photonic quantum computing.
- Quantum Annealing HW: Hardware designed for optimization problems using quantum annealing, where the system evolves toward a low-energy solution, rather than universal quantum computation.
- Hybrid Solvers: Algorithms or systems that combine quantum and classical computing to solve problems, often using quantum devices for subproblems within a classical optimization framework.
- Superconducting Qubit HW & Scaling (Quantum Computers): Quantum hardware based on superconducting circuits cooled near absolute zero, with active research into scaling up the number of stable qubits for practical computation.
- Silicon Spin Qubits & Quantum Dot / CMOS-Based HW: Quantum hardware that uses electron or nuclear spins in silicon quantum dots, aiming for scalability through integration with CMOS semiconductor technology.
- Error Correction / Fault Tolerance / Quality Control: Techniques and systems that detect and correct quantum errors (caused by noise and decoherence), and ensure computations remain reliable as systems scale.
Just asked a few people in the field, short comments: D-Wave is a scam, and photon detection is industrialised, and quantum-safe communication closer to the product
hello Sergey,
many thanks for your comment, will update the map with these inputs,