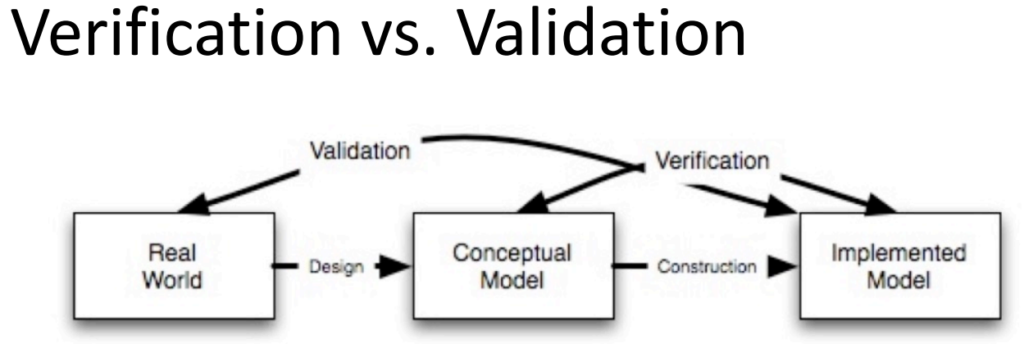
All models require to be validated and verified.
- Verification is the process of making sure your conceptual model matches your implemented model.
- Validation is the process of making sure your implemented model corresponds to the real world.
Verification
- Communication is essential to verification
- Often the model developer and the model author are not the same person.
- Reducing / eliminating the gap between developer and author improves verification.
- We need a common language to describe conceptual models that is recognized by both authors and developers.
Validation
Ensuring that the implemented model corresponds to reality.
- All models are simplifications of reality.
- “All models are wrong but some are useful.” – George E. P. Box.
Types of validation
- Macro-Validation: Comparing aggregate results at many different levels.
- Are the patterns of adoption similar?
- Micro-Validation:
- Comparing individual rules: Do consumers use the same information when deciding whether or not to adopt?
- Comparing individual properties: Are the properties similar?
- Face Validation: Do the general ideas about behavior and properties compare to real-world phenomena?
- Empirical Validation: Does data from the model correspond to real-world data?