SCOR is a process reference model is considered as the cross-industry de-facto standard diagnostic tool for supply chain management. It has been developed by the Supply-Chain Council (SCC).
SCOR is a process reference model is considered as the cross-industry de-facto standard diagnostic tool for supply chain management. It has been developed by the Supply-Chain Council (SCC).
SCOR is a management tool, spanning from the supplier’s supplier to the customer’s customer. The model has been developed by the members of the Council on a volunteer basis to describe the business activities associated with all phases of satisfying a customer’s demand.
The model is based on 3 major “pillars”:
- Process modeling
- Performance measurements
- Best practices
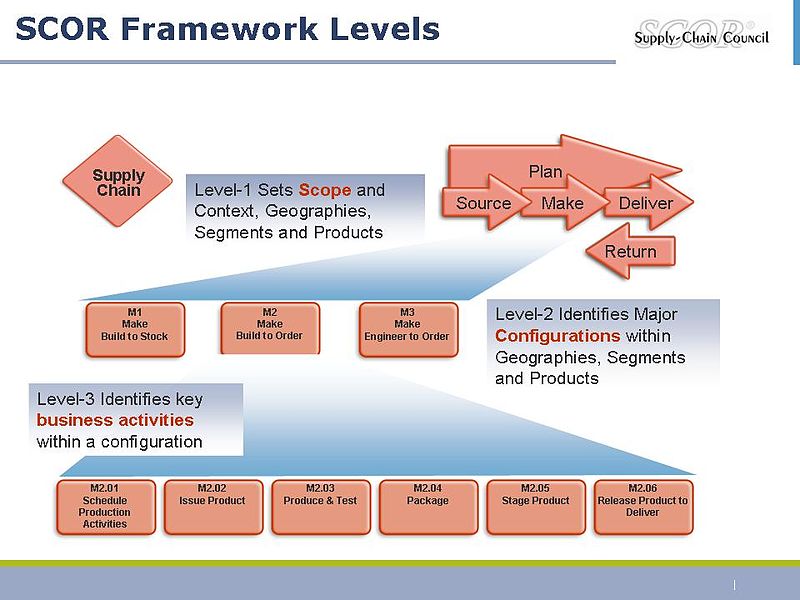
Pilla #1.- Process Modeling. SCOR is based on five distinct management processes: Plan, Source, Make, Deliver, and Return.
- Plan – Processes that balance aggregate demand and supply to develop a course of action which best meets sourcing, production, and delivery requirements.
- Source – Processes that procure goods and services to meet planned or actual demand.
- Make – Processes that transform product to a finished state to meet planned or actual demand.
- Deliver – Processes that provide finished goods and services to meet planned or actual demand, typically including order management, transportation management, and distribution management.
- Return – Processes associated with returning or receiving returned products for any reason. These processes extend into post-delivery customer support.
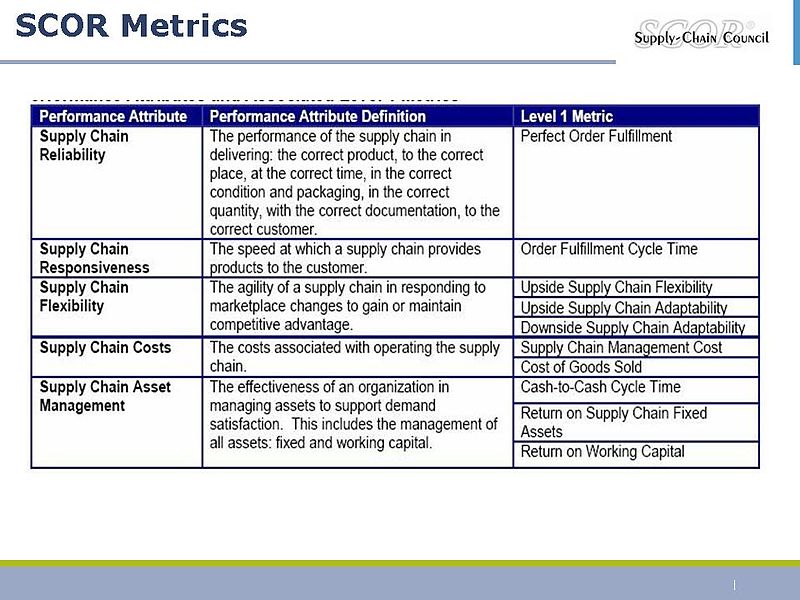
 Pilar #2.- Performance measurement.
Pilar #2.- Performance measurement.
- The SCOR model contains more than 150 key indicators that measure the performance of supply chain operations.
- These are organized in a hierarchical structure. Level 1 metrics are at the most aggregated level, and are typically used by top decision makers.
- The metrics are used in conjunction with performance attributes (characteristics that permit the analysis and evaluation against other supply chains with competing strategies).
Pillar #3.- Best Practices. Over 430 executable practices.
The SCOR model defines a best practice as a current, structured, proven and repeatable method for making a positive impact on desired operational results.
- Current – Must not be emerging (bleeding edge) and must not be antiquated
- Structured – Has clearly stated Goal, Scope, Process, and Procedure
- Proven – Success has been demonstrated in a working environment.
- Repeatable – The practice has been proven in multiple environments.
- Method- Used in a very broad sense to indicate: business process, practice, organizational strategy, enabling technology, business relationship, business model, as well as information or knowledge management.
- Positive impact on desired operational results The practice shows operational improvement related to the stated goal and could be linked to Key Metric(s). The impact should show either as gain (increase in speed, revenues, quality) or reduction (resource utilizations, costs, loss, returns, etc.).
Reference here, and from the Wikipedia here.
I’m happy, I’m having some time this week to read and learn.